Overview
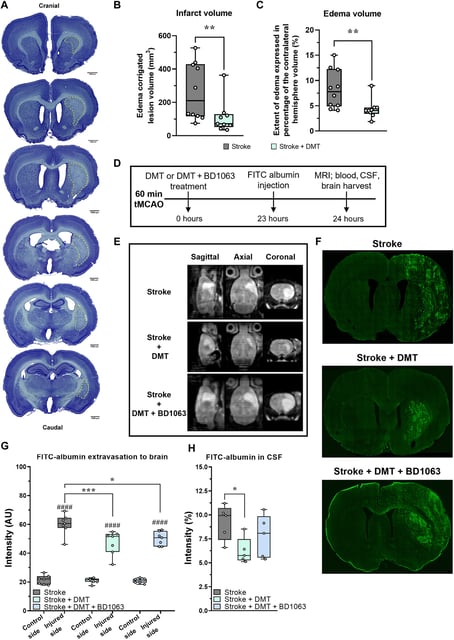
- Researchers from HUN-REN BRC and Semmelweis University report that DMT cut infarct volume and brain swelling in a rat transient middle cerebral artery occlusion model.
- Treatment restored tight-junction structure and blood–brain barrier function and improved astroglial cell performance in vivo and in vitro.
- DMT suppressed proinflammatory cytokine release in brain endothelial and peripheral immune cells and dampened microglial activation via the Sigma-1 receptor.
- The authors frame the compound as a possible adjuvant to limited existing stroke therapies based on its dual vascular and anti-inflammatory actions.
- Early clinical evaluations of DMT for post-stroke recovery are underway, though dosing, safety, and efficacy in humans remain unproven.