Overview
- Researchers from the HUN-REN BRC Institute of Biophysics and Semmelweis University report the findings in Science Advances.
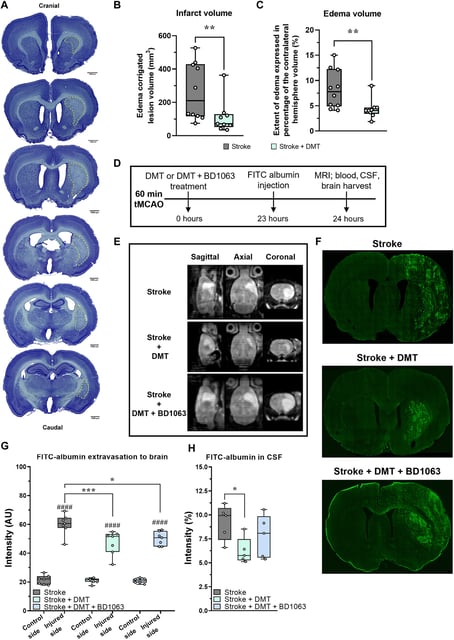
- In a rat stroke model, DMT significantly reduced infarct volume and cerebral edema.
- Treatment restored blood–brain barrier structure and function and improved astroglial performance in animal and cell studies.
- DMT suppressed inflammatory cytokine production and reduced microglial activation through Sigma-1 receptors.
- The authors propose DMT’s dual vascular and anti-inflammatory actions could complement current stroke care, with human efficacy and safety still being evaluated in trials.