Overview
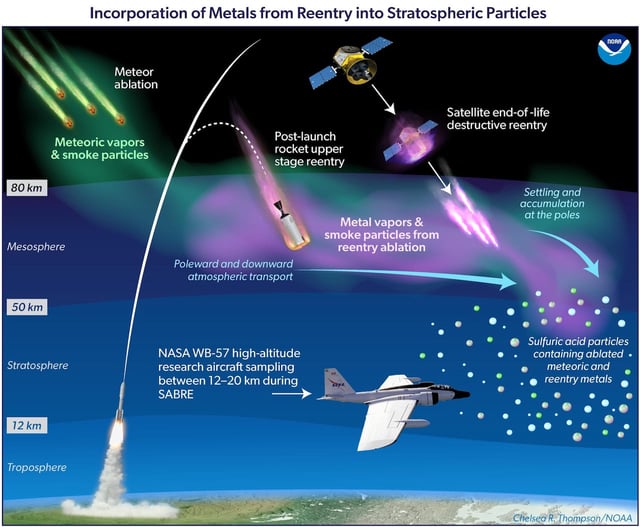
- Researchers found that aluminum oxides from satellite re-entries have surged eightfold since 2016.
- The particles trigger chemical reactions that deplete the ozone layer, which protects Earth from harmful UV radiation.
- SpaceX's Starlink and other megaconstellations are major contributors to this pollution.
- Scientists call for more research to understand the long-term impacts on atmospheric health.
- Current satellite deorbiting practices lack regulations to mitigate environmental damage.