Overview
- The team synthesized the cyclo[48]carbon as a [4]catenane by linking three macrocyclic rings onto cobalt-protected polyyne precursors and then removing the metal groups to unmask the carbon ring.
- Mass spectrometry, UV–visible and Raman spectroscopy, along with a single intense 13C NMR resonance for all 48 sp1 carbons, provided convergent evidence for the symmetrical catenane structure in solution.
- In deuterated dichloromethane at 20 °C and concentrations up to 300 µM, the protected catenane exhibits a half-life of about 92 hours, enabling extended spectroscopic analysis under ambient lab conditions.
- Researchers also detected an unprotected cyclo[48]carbon species at low concentration, estimating a half-life of approximately one hour and noting its UV–visible spectrum matches that of the protected form.
- Published in Science, this represents only the second new molecular carbon allotrope accessible under normal laboratory conditions since fullerenes and paves the way for crystallization, X-ray diffraction and studies of its reactivity and electronic properties.
![Left: Chemical structure of the cyclo[48]carbon [4]catenane. RIGHT: Space-filling representation.](/cdn-cgi/image/onerror=redirect,width=640,height=640,format=webp/https://storage.googleapis.com/uploads.mongoosehq.com/url/media/39553022/6c3674fcd473fd05642db44e4276e64826a8d1749d712d43258bd4df826e6736)
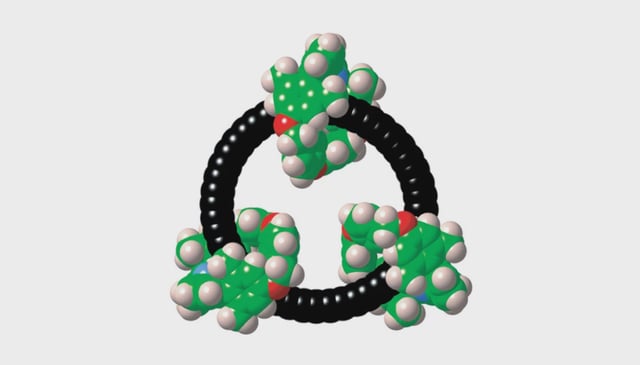
![Chemical structure of the cyclo[48]carbon [4]catenan. Image credit: Harry Anderson.](/cdn-cgi/image/onerror=redirect,width=640,height=640,format=webp/https://storage.googleapis.com/uploads.mongoosehq.com/url/media/39774518/2f353f6e0fe96a88c12529f88985b73646f70a04416891d144192617b919bd3c)