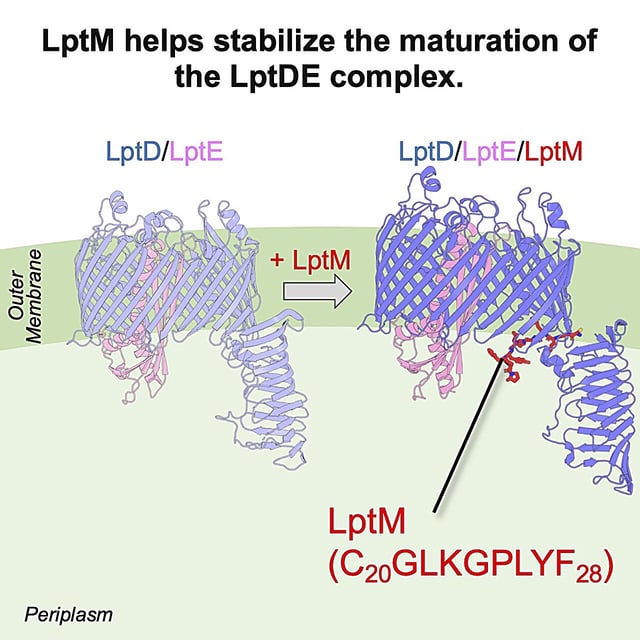
Overview
- A preprint posted on July 16 shows that LptM binds a folded LptD intermediate through a segment of fewer than ten amino acids to stabilize the LptDE complex.
- Cryo-electron microscopy provides a high-resolution view of the LptM–LptDE interface in Escherichia coli.
- LptM’s late-stage role fine-tunes LptD maturation and secures lipopolysaccharide transport across the outer membrane.
- Mutational analysis pinpoints the essential amino-acid motif within LptM responsible for its stabilizing function.
- These insights position the LptDE translocon as a compelling target for novel antibiotics against resistant Gram-negative bacteria.