Overview
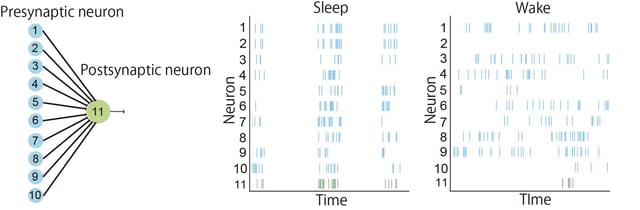
- Researchers used detailed neural network simulations with Hebbian and STDP rules to model cortical synaptic dynamics across sleep-wake cycles.
- The model shows that large differences in neuronal firing rates favor wake-time synaptic potentiation while small differences enable strengthening during sleep.
- This unified framework reconciles the Synaptic Homeostasis Hypothesis and Wake Inhibition, Sleep Excitation models by linking activity thresholds to synaptic outcomes.
- By charting the boundary between downscaling and potentiation, the study provides theoretical support for ‘sleep learning’ possibilities.
- The findings offer a computational platform for probing memory consolidation, sleep-related psychiatric disorders and bioinspired learning algorithms.