Overview
- Using long-read, telomere-to-telomere methods, researchers produced the first complete assemblies of human Robertsonian chromosomes.
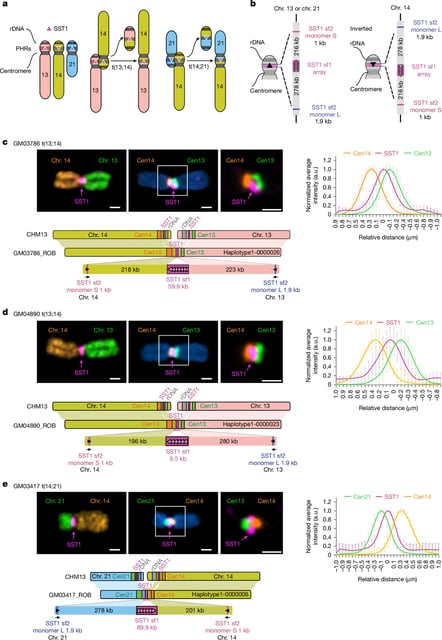
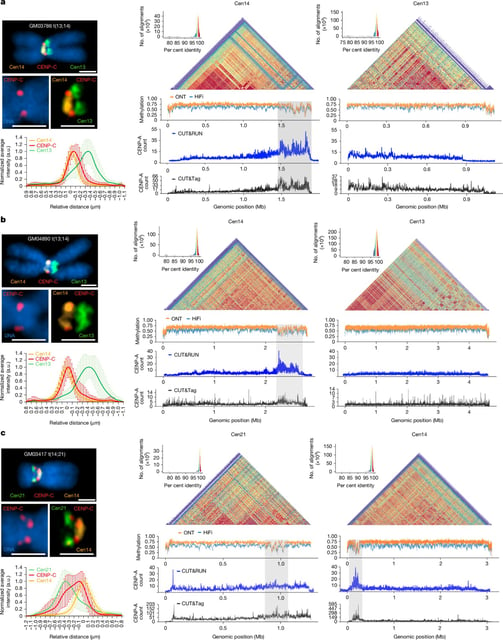
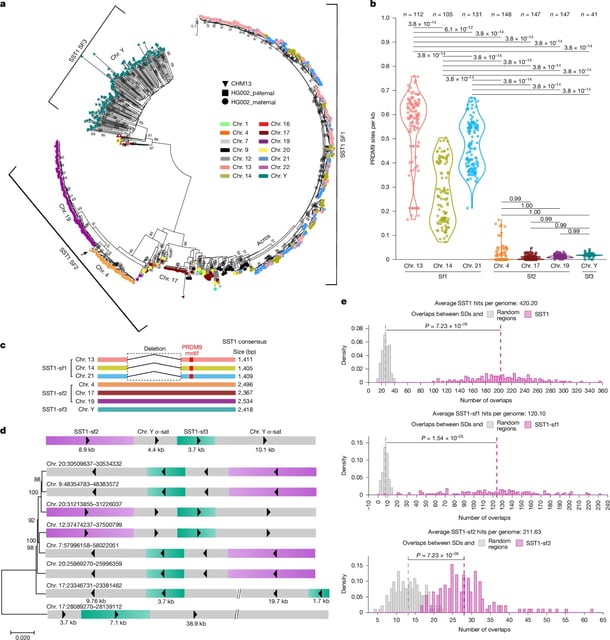
- They pinpointed a shared fusion breakpoint within the repetitive SST1 sequence near centromeres, a site not previously mapped in humans.
- Three sequenced cell lines carried 14;13 or 14;21 fusions drawn from a healthy individual, a person with Down syndrome, and an individual with recurrent miscarriages.
- Analyses found that one of the two centromeres on the fused chromosome is epigenetically silenced, which enables proper segregation during cell division.
- The team reports orientation of SST1 on chromosome 14 helps permit fusion with chromosomes 13 or 21 and outlines follow-up work on population variation and evolutionary implications.