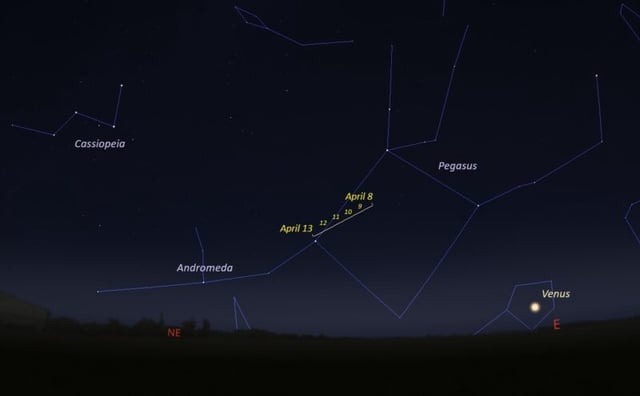
Overview
- Comet SWAN25F, discovered in late March 2025 using SOHO spacecraft data, is now visible in the constellation Pegasus during pre-dawn hours.
- The comet's brightness has increased significantly, currently at magnitude 8, and is projected to potentially reach magnitude 4–5 by early May.
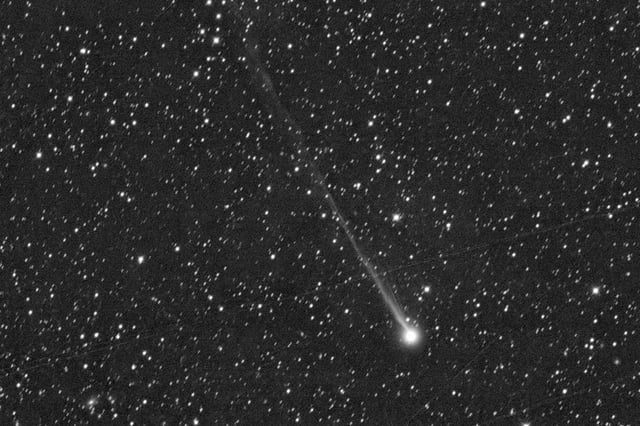
- Its green coma, caused by diatomic carbon, and a long tail over 2 degrees in length highlight active outgassing as it nears the sun.
- Global observations, including images from Arizona, Austria, and the UAE, confirm its trajectory and rapid brightening ahead of its closest approach to the sun on May 1, 2025.
- If it survives its perihelion, the comet may transition to evening visibility, offering a rare opportunity for observation without optical aid.