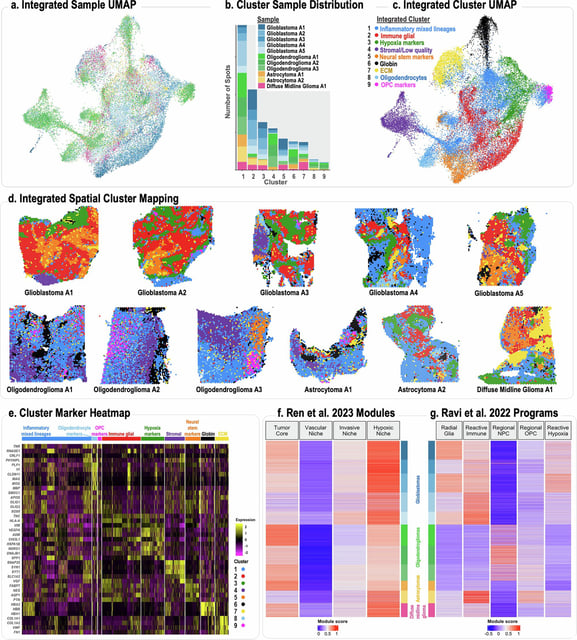
Overview
- City of Hope scientists characterized extrachromosomal DNA near chromosomes to build a spatial map of glioma cells that predicts how mutated genes reshape tumor behavior.
- The analysis revealed that ecDNA drives rapid oncogene proliferation outside chromosomes, fueling genetic instability and diverse cell populations within brain tumors.
- Researchers found that elevated ecDNA levels and oncogenic proteins such as EGFR or p53 induce a hypoxic tumor microenvironment associated with resistance to therapy and poorer outcomes.
- By integrating spatial transcriptomics with bulk RNA and DNA sequencing, the team traced subclonal relationships among tumor cells and highlighted potential therapeutic targets.
- Supported by the NIH’s NCATS program, the Nature Communications paper outlines an analytical framework to advance precision oncology research.