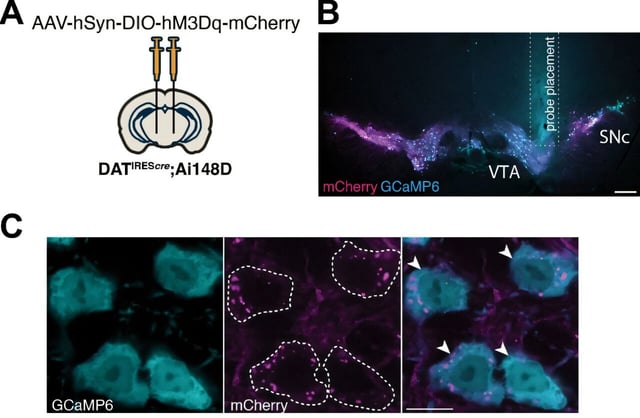
Overview
- Researchers chronically activated midbrain dopamine neurons using a DREADD receptor with clozapine-N-oxide provided in drinking water.
- Within days, mice showed disrupted light–dark activity; by one week, axons degenerated; by about a month, dopamine neurons began to die.
- Degeneration was preferential in the substantia nigra neurons that control movement, with relative sparing of dopamine neurons tied to motivation and emotion.
- Overactivation drove sustained baseline calcium increases and reduced expression of genes governing dopamine metabolism, calcium handling, and stress responses.
- Similar molecular patterns were detected in early human Parkinson’s brain samples, and investigators suggest activity modulation by drugs or deep brain stimulation as a hypothesis requiring human testing.