Overview
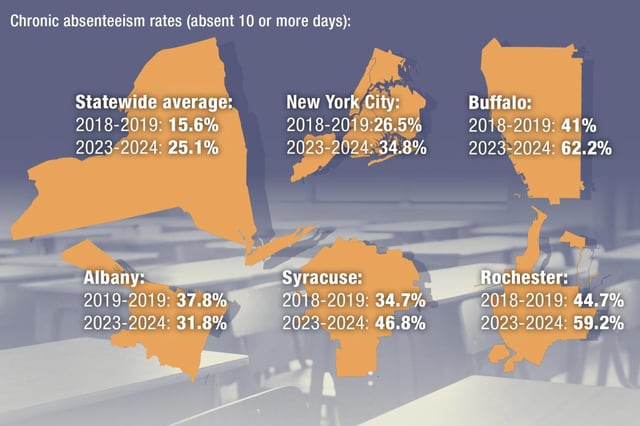
- The chronic absenteeism rate in NYC public schools rose to 34.8% in the 2023-24 school year, up from 26.5% before the pandemic, affecting over 300,000 students.
- Low-income, Black, Hispanic, and students in temporary housing are disproportionately impacted, with absenteeism rates exceeding 40% in these groups.
- Chronic absenteeism correlates with lower academic performance, higher dropout rates, and long-term social and economic challenges for students.
- While NYC spends more per student than any other state, student performance in math and reading remains below pre-pandemic levels, highlighting systemic inefficiencies.
- Charter schools and certain public schools have implemented targeted strategies, such as family engagement and attendance incentives, to reduce absenteeism successfully.