Overview
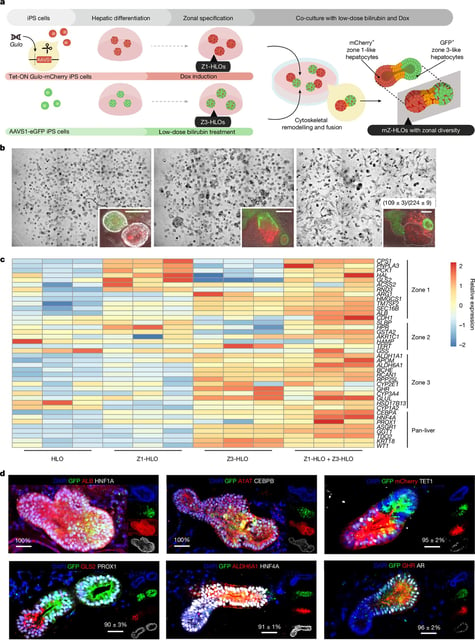
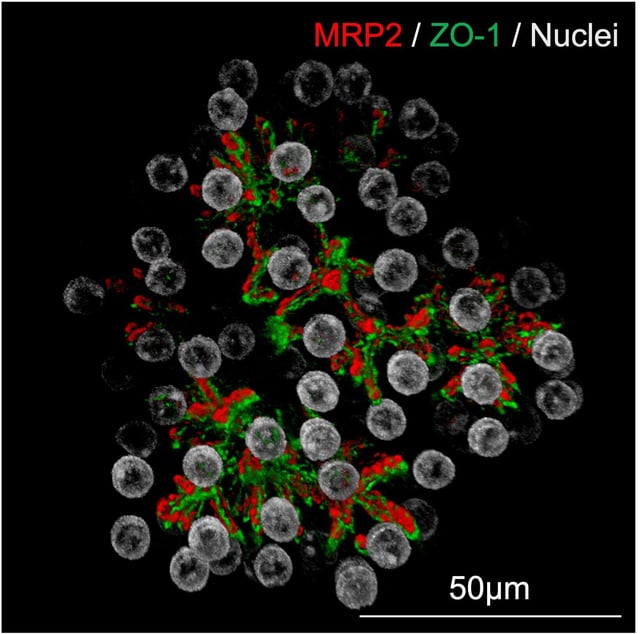
- Cincinnati Children’s researchers developed multi-zonal liver organoids that mimic human liver microarchitecture, doubling survival in rodents with bile duct injuries.
- Keio University achieved a million-fold proliferation of hepatocyte organoids in weeks, retaining key liver functions such as glucose and bile acid production.
- Keio organoids successfully replaced liver cells and restored function in immunocompromised mice, demonstrating potential for regenerative therapies.
- Short-term applications include using these advanced organoids to accelerate drug metabolism and toxicity testing for diseases like diabetes and liver injury.
- Future goals involve scaling organoid cultures to billions of cells and exploring patient-specific liver tissue regeneration to reduce reliance on organ donations.