Overview
- Exhaled breath analysis can reveal chemical markers of diseases, including lung cancer, through compounds like isoprene.
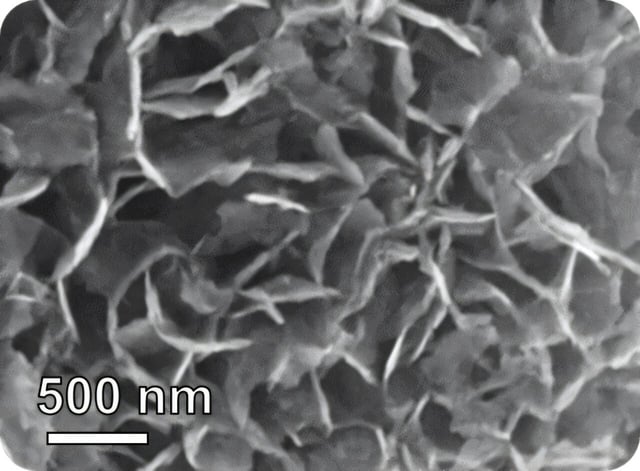
- The newly developed Pt@InNiOx nanoflake sensors detect isoprene at levels as low as 2 parts per billion, offering unprecedented sensitivity.
- These sensors selectively respond to isoprene over other volatile compounds present in breath, ensuring accurate readings.
- In practical tests, the portable sensing device distinguished lung cancer patients from healthy individuals based on isoprene levels.
- Further research and clinical trials are needed to commercialize this technology for non-invasive lung cancer screening.