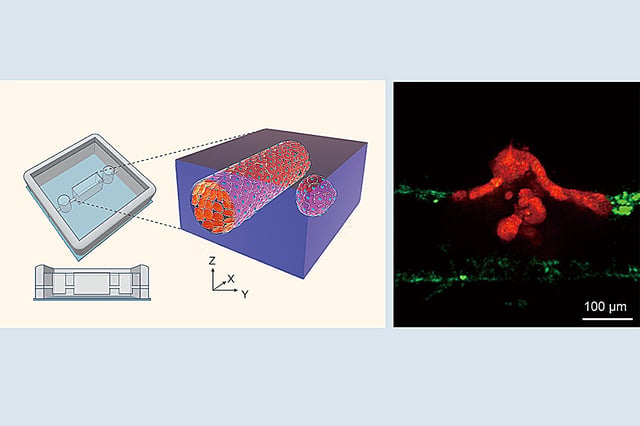
Overview
- A novel 3D tumor-microvessel on-a-chip model has captured real-time tumor cluster migration and vascular entry for the first time.
- Tumor clusters induce TGF-β and activin-driven endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT), weakening blood vessel walls to enable entry.
- Once inside the bloodstream, these cohesive clusters disperse, enhancing their metastatic potential and ability to colonize distant sites.
- The study highlights the superiority of tumor clusters over single cells in driving metastasis, a leading cause of cancer mortality.
- This platform provides a scalable tool for screening anti-metastatic drugs targeting the mechanisms of vascular infiltration.