Overview
- In fMRI tests, people identified with specific musical anhedonia showed normal reward responses to monetary wins but not to music.
- The team screens individuals using the Barcelona Music Reward Questionnaire and confirms low music response with physiological measures.
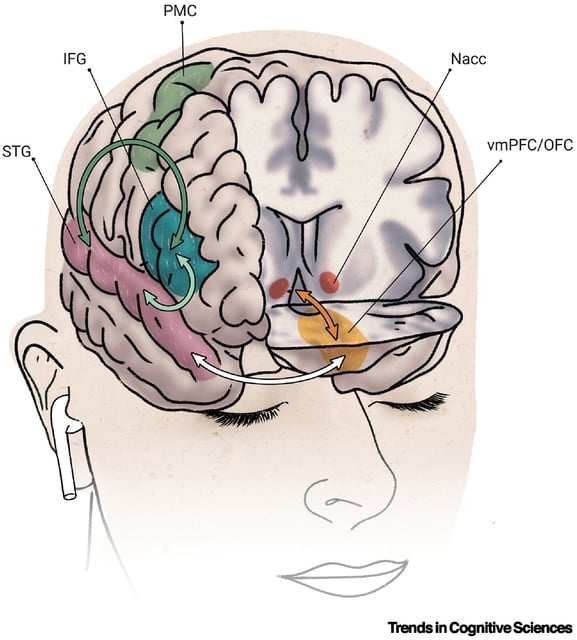
- Auditory and reward regions function normally on their own in affected people, but their communication appears disrupted.
- Estimates cited in the review suggest roughly 5%–10% of people are indifferent to music, whereas about a quarter are unusually responsive.
- Preliminary genetic work points to about half of the variance in musical reward sensitivity being heritable, and prior stimulation studies indicate connectivity can be modulated.