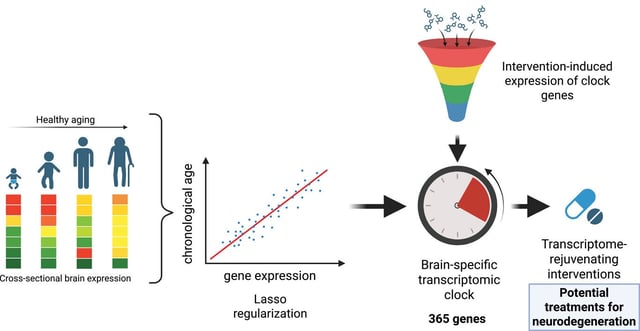
Overview
- An international team built a brain-specific transcriptomic clock using a Lasso-regularized model on human samples aged 20 to 97 to derive 365 gene markers of cellular brain age.
- Application of the clock to neural progenitor cells and neurons treated with thousands of compounds identified 453 interventions that reverse the transcriptomic aging signature.
- In proof-of-concept trials, three top candidates reduced anxiety, improved spatial memory and shifted cortical gene expression toward a younger profile in aged mice.
- Higher biological brain age measured by the clock correlates with neurodegenerative severity in patient samples, underscoring its relevance for therapeutic discovery.
- Next steps focus on validating the predicted candidates across diverse biological systems to determine their efficacy and safety for neuroprotective drug development.