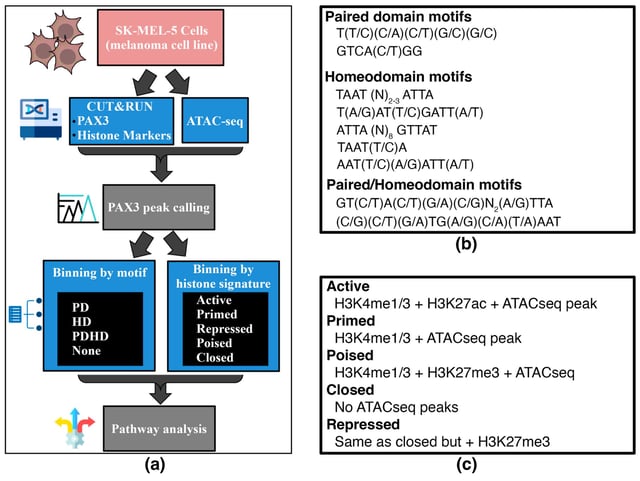
Overview
- The study reveals that PAX3 primarily uses its paired domain (PD) to bind DNA and activate genes critical for melanoma cell growth and survival.
- PAX3 predominantly acts as a gene activator in melanoma, contrasting with prior assumptions that it also functioned as a repressor.
- A novel computational modeling approach allowed researchers to map PAX3’s DNA binding sites with unprecedented precision.
- The findings highlight the paired domain as a promising target for drug development, with efforts underway to design selective inhibitors.
- Therapeutic strategies must balance targeting PAX3’s pathological role in melanoma while preserving its essential function in normal melanocyte development.