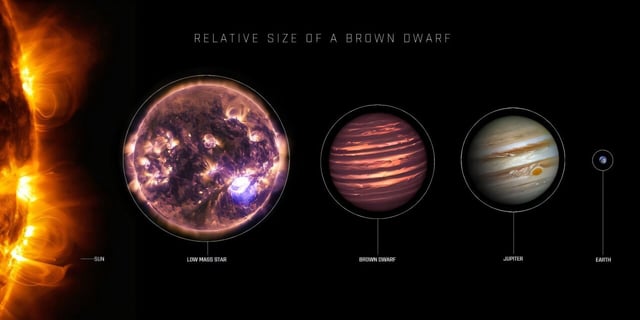
Overview
- A July paper in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics formalized a model of ‘dark dwarfs’, brown dwarfs heated continuously by self-annihilating dark matter.
- High dark matter density near galactic centers could enable sufficient particle capture inside these objects to sustain steady heat output.
- Dark dwarfs would maintain constant luminosity, radius and temperature and uniquely preserve their initial lithium-7, unlike normal brown dwarfs.
- Detecting a single dark dwarf through its lithium-7 spectral signature would strongly support the existence of heavy, self-interacting dark matter particles such as WIMPs.
- Teams are now planning targeted lithium-7 surveys and infrared observations with the James Webb Space Telescope to seek these theoretical sub-stellar objects.