Overview
- Aspergillus fumigatus detections have surged in mid-June across Florida, Texas, California, Louisiana and Georgia with reports of environmental spores in soil and compost piles.
- The World Health Organization designated the fungus a critical-priority threat due to its growing resistance to existing antifungal drugs and high fatality rates in immunocompromised patients.
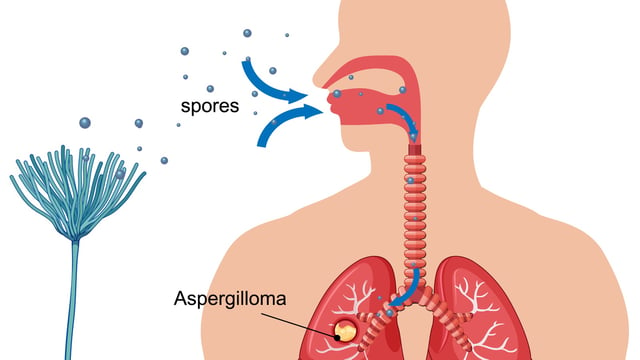
- Aspergillosis cases range from allergic and chronic lung conditions to invasive disease that can spread to the brain, kidneys and other organs with symptoms like fever, cough and shortness of breath.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advises high-risk individuals to avoid dusty areas, wear N95 masks during outdoor soil-disturbing activities and use protective clothing to reduce spore inhalation.
- Public health researchers emphasize the need for enhanced environmental monitoring, faster diagnostic tests and the development of new antifungal therapies to curb the pathogen’s expanding reach.