Overview
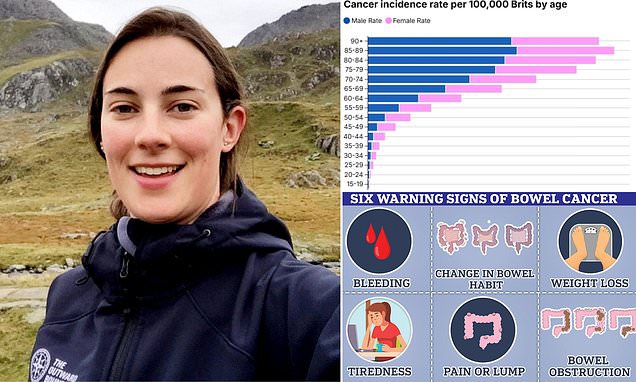
- Data from the National Cancer Institute’s SEER registry show appendix cancer rates have tripled among those born around 1980 and quadrupled for those born around 1985 compared with the 1945 birth cohort.
- The rise in appendix cancer reflects a broader increase in gastrointestinal cancers among younger adults across recent generations.
- Researchers point to a combination of factors—rising obesity, dietary changes, environmental exposures and genetic predispositions—as potential drivers of the trend.
- Most appendix cancers are discovered incidentally during or after appendectomies, leading to late-stage diagnoses because symptoms like abdominal pain and bloating are nonspecific.
- Experts are calling for heightened vigilance among clinicians and public education to promote earlier detection and improve patient outcomes.