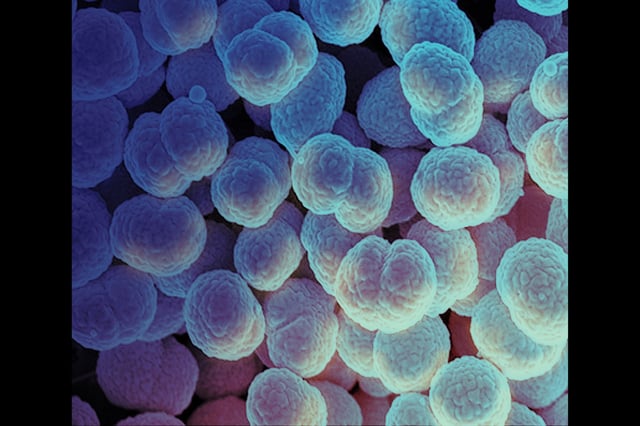
Overview
- A woman in her 50s in Anchorage died this spring after untreated gonorrhea spread to her bloodstream and heart, causing septic shock and endocarditis.
- Reported cases of disseminated gonococcal infection in Alaska climbed from two in 2022 to 24 in 2024, with eight cases recorded in the first half of 2025.
- Officials suspect that emerging Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains with milder initial symptoms are contributing to the recent spike in systemic infections.
- Many recent patients showed few or no genital symptoms and sometimes tested negative on standard urine and swab tests before developing DGI.
- The Alaska Department of Health advises people with new or multiple sexual partners to undergo gonorrhea testing every three to six months and is monitoring antibiotic-resistant variants after Canada’s first super gonorrhea case.