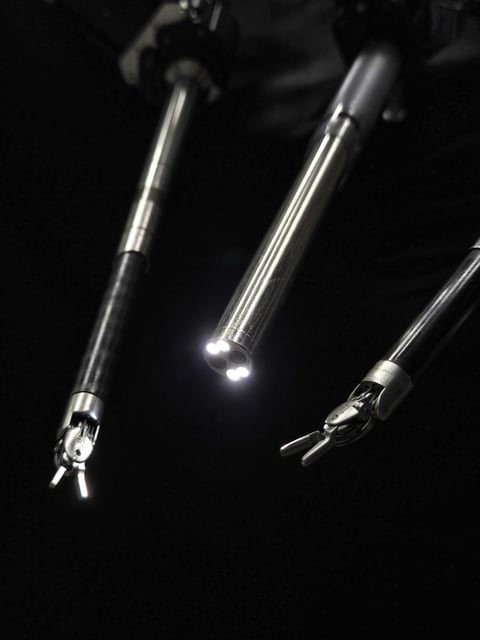
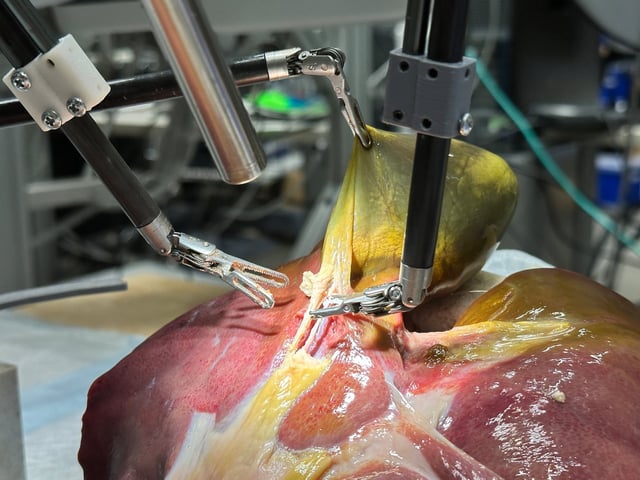
Overview
- The Surgical Robot Transformer-Hierarchy autonomously executed all 17 steps of a gallbladder removal on lifelike models, adapting to dye-altered tissues and randomized starting positions
- Built on a transformer architecture similar to ChatGPT, the system learned complete surgical workflows through multimodal imitation learning of annotated procedure videos
- During trials, the robot responded to real-time spoken commands from the surgical team, mirroring mentor-trainee interactions and refining its performance on the fly
- Backed by U.S. federal funding and published in Science Robotics, this milestone shifts robotic surgery from discrete task execution toward holistic procedural understanding
- The Johns Hopkins–led team now aims to broaden the robot’s capabilities to additional operations while navigating safety protocols, regulatory review and clinical integration challenges