Overview
- Researchers at MIT and McMaster report enterololin in Nature Microbiology as a narrow-spectrum agent that suppresses Enterobacteriaceae linked to Crohn’s disease flare-ups.
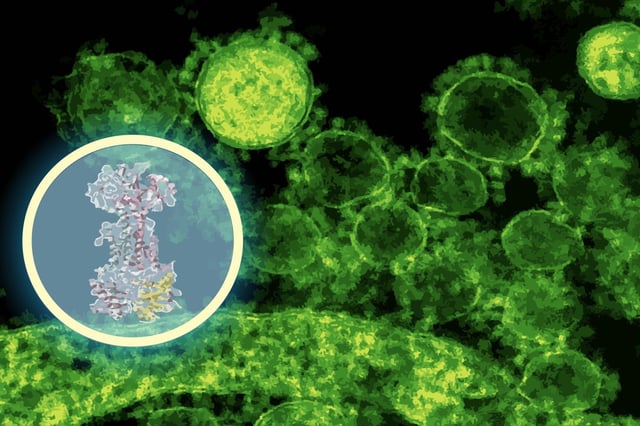
- DiffDock predicted binding to the LolCDE lipoprotein-transport complex in minutes, providing a concrete lead that directed subsequent lab tests.
- Mechanism validation came from evolved E. coli resistance mutations mapping to lolCDE, RNA sequencing signatures, and CRISPR knockdowns consistent with lipoprotein transport disruption.
- In mouse models of Crohn’s-like inflammation, enterololin targeted E. coli, accelerated recovery, and preserved the gut microbiome compared with vancomycin.
- Stoked Bio has licensed the compound for optimization with clinical trials projected within the next few years, and the team released sequencing data and DiffDock-L code publicly.