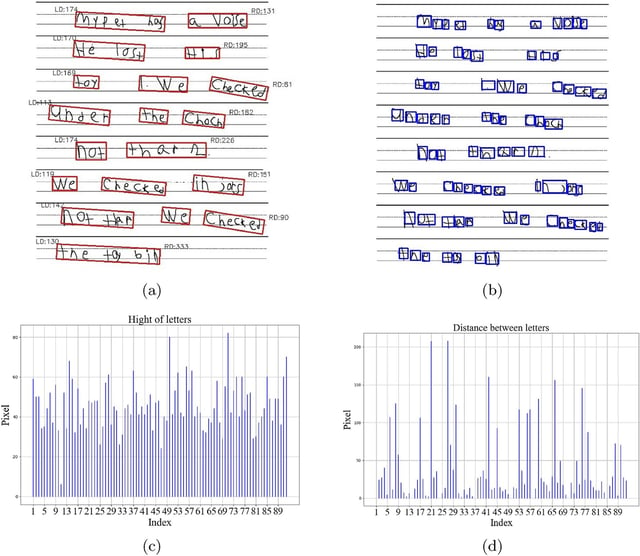
Overview
- The UB-led study has completed data collection and model development, now focusing on validating AI performance against the Dysgraphia and Dyslexia Behavioral Indicator Checklist (DDBIC).
- The project integrates motor, visual, linguistic, and cognitive markers to develop a comprehensive early screening tool for neurodevelopmental disorders.
- Ethically collected and anonymized handwriting samples from K–5 students in Reno are being used to train and test the AI models.
- The study builds on decades-old handwriting recognition research, repurposing techniques originally developed for postal sorting.
- Researchers aim to streamline early detection of dyslexia and dysgraphia, addressing specialist shortages and improving access in resource-limited areas.