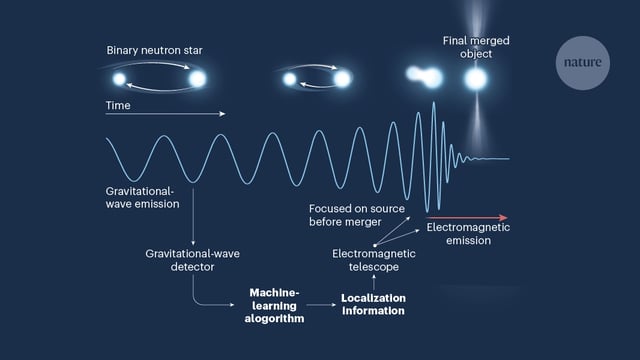
Overview
- The DINGO-BNS algorithm uses machine learning to analyze gravitational waves from binary neutron star mergers with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
- This method reduces analysis time from an hour to one second, allowing astronomers to quickly locate merger events and optimize telescope observations.
- The algorithm improves localization accuracy by 30%, enabling better detection of electromagnetic signals like kilonovas associated with neutron star mergers.
- Real-time analysis could allow telescopes to observe the merger process and its aftermath, offering new insights into heavy element formation and cosmology.
- The approach combines advanced machine learning techniques with physics knowledge, potentially setting a new standard for gravitational wave data analysis.