Overview
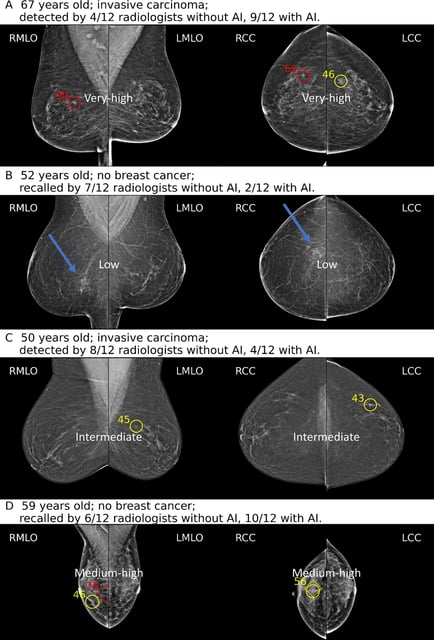
- In a July reader study, 12 radiologists reviewed 150 screening mammograms with and without AI assistance to map gaze patterns and diagnostic performance.
- AI assistance improved sensitivity from 81.7% to 87.2% and specificity from 89.0% to 91.1%, producing a significant AUC rise from 0.93 to 0.97.
- Eye-tracking data showed radiologists fixated on true lesion regions for 5.4 seconds with AI guidance versus 4.4 seconds without and reduced normal-area coverage from 11.1% to 9.5%.
- Radiologists modulated their review pace based on AI suspicion scores, fast-tracking low-risk cases and conducting deeper analyses of high-suspicion examinations.
- Researchers are launching follow-up studies to optimize alert timing and develop uncertainty-prediction tools that aim to maximize benefits and reduce the risk of overreliance.