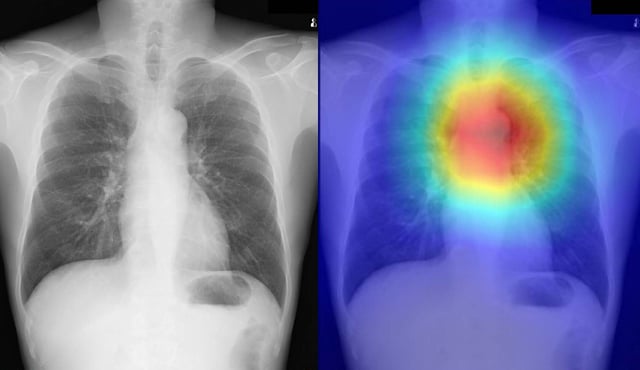
Overview
- Osaka Metropolitan University researchers reported the findings in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
- On a separate test set, the model reached an AUC of 0.964 with 0.941 sensitivity and 0.891 specificity, outperforming physicians reviewing the same images.
- Training data included 207 chest X-rays from 144 achalasia patients and 240 from matched controls, with validation on 17 achalasia and 64 non-achalasia images.
- Model heatmaps concentrated on the esophageal region, aligning with expected signs such as dilation and tortuosity visible on radiographs.
- The team notes current diagnostics are invasive and that diagnosis often takes about 6.5 years from symptom onset, indicating potential for earlier detection.