Overview
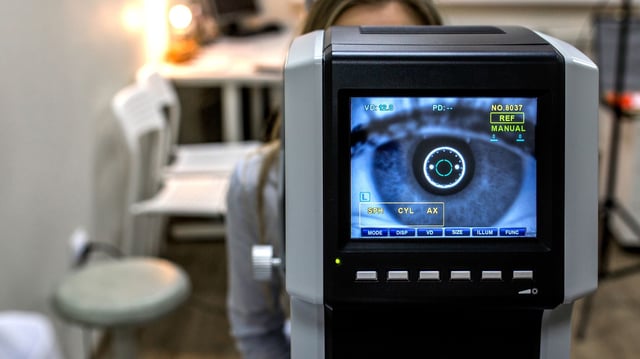
- The AI system analyzed routine NHS retinal scans from over 1,200 diabetic patients and achieved 70 percent accuracy in forecasting major cardiovascular events over ten years.
- When paired with standard clinical risk scores and genetic testing, the model’s predictive accuracy climbed to 73 percent.
- Patients in the top fifth for three-year increases in AI-derived risk scores faced a 54 percent greater likelihood of heart attack or stroke.
- The technology delivers personalized risk predictions in under a second by leveraging existing diabetic retinopathy screening infrastructure.
- Researchers are planning broader clinical trials to validate the tool’s robustness, scalability, and integration into routine care.