Overview
- AI-designed de novo protein “minibinders” enabled engineered T cells to eliminate NY-ESO-1–positive melanoma cells in vitro with high specificity.
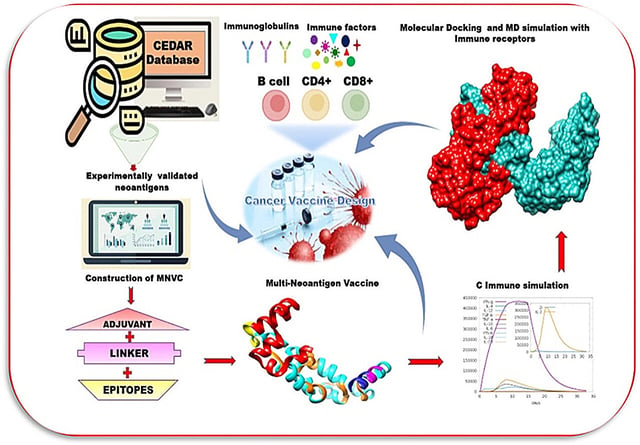
- An in silico vaccine construct combines eight AI-prioritized neoantigens with linkers and an adjuvant, showing strong predicted immunogenicity alongside allergenicity and toxicity filters.
- The computational workflow uses RFdiffusion, sequence-generation models and virtual cross-reactivity screening to cut therapeutic design timelines from years to weeks.
- Collaborating teams at DTU and partner institutes are gearing up for in vivo safety and efficacy assessments of both protein binders and vaccine constructs in animal models.
- Investigators anticipate initial human trials within five years as part of a streamlined, personalized immunotherapy pipeline for melanoma.