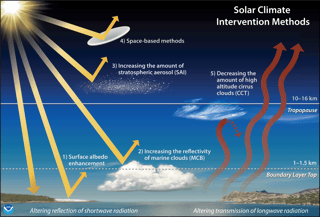
Solar geoengineering, or solar radiation modification (SRM), is a type of climate engineering in which sunlight (solar radiation) would be reflected back to outer space to limit or reverse human-caused climate change. It is not a substitute for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, but would act as a temporary measure to limit warming while emissions of greenhouse gases are reduced and carbon dioxide is removed. The most studied methods of SRM are stratospheric aerosol injection and marine cloud brightening. Solar geoengineering appears able to prevent some or much of climate change temperature increases. Climate models consistently indicate that it is capable of returning global, regional, and local temperatures and precipitation closer to pre-industrial levels. Solar geoengineering's principal advantages are the speed with which it could be deployed and become active and the reversibility of its direct climatic effects, although the latter varies depending on method, with some concerns raised over stratospheric aerosol injection. Proposed methods of solar geoengineering may be atmospheric, terrestrial, or space-based. Stratospheric aerosol injection appears technically feasible and inexpensive in terms of direct financial costs, though still out of reach for individuals, small states, or other non-state rogue actors; it would instead be the exclusive domain of large national economies or coalitions including at least one such economy. Space-based propositions are only theoretical, being too expensive and infeasible to implement in the next few decades. Solar geoengineering would not directly reduce carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere, and thus does not address ocean acidification or air pollution caused by high levels of atmospheric CO2. Solar geoengineering's excessive and/or poorly distributed use, or sudden and sustained termination, could pose serious environmental risks. Other negative impacts are possible and more research is required to thoroughly address such impacts. Governing solar geoengineering is challenging for multiple reasons, including that few countries would likely be capable of doing it alone. From Wikipedia