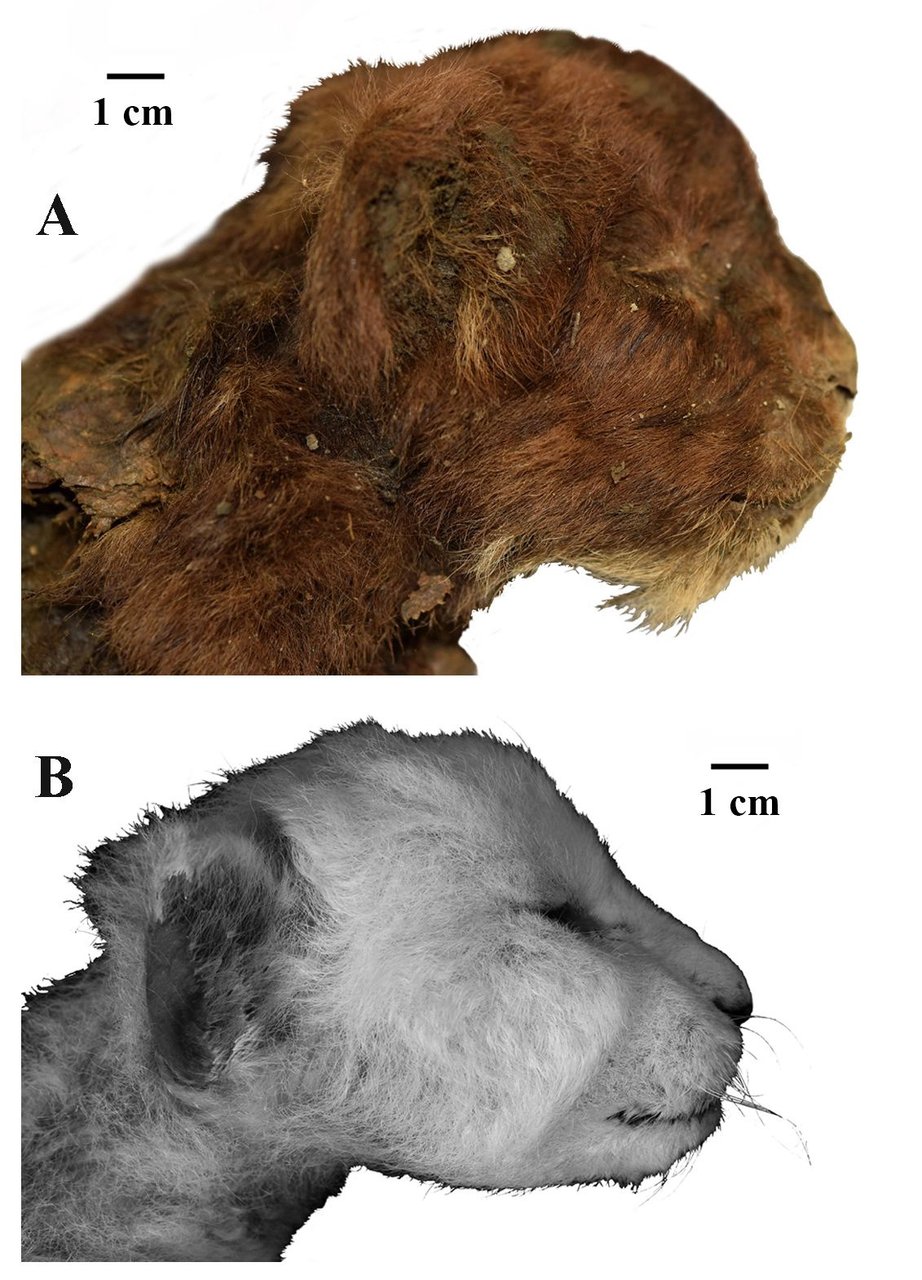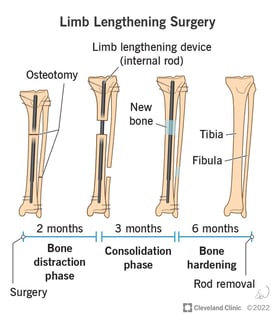
A limb (from the Old English lim, meaning "body part") or leg is a jointed, muscled appendage that tetrapod vertebrates use for weight-bearing and terrestrial locomotion such as walking, running and jumping, for paddle-swimming, or for grasping and climbing. The distalmost portion of a limb is known as its extremity. The limbs' bony endoskeleton, known as the appendicular skeleton, is homologous among all tetrapods. All tetrapods have four limbs that are organized into two bilaterally symmetrical pairs, with one pair at each end of the torso. The cranial pair are known as the forelimbs or front legs, and the caudal pair the hindlimbs or back legs. In animals with more upright posture (mainly hominid primates, particularly humans), the forelimbs and hindlimbs are often called upper and lower limbs, respectively. The fore-/upper limbs are connected to the thoracic cage via the shoulder girdles, and the hind-/lower limbs are connected to the pelvis via the hip joints. Many animals, especially the arboreal species, have prehensile forelimbs adapted for grasping and climbing, while some (birds and bats) have expanded forelimbs (and sometimes hindlimbs as well) with specialized feathers or membranes to achieve lift and fly. Some animals (mostly primates) can also use hindlimbs for grasping. In the human body, the upper and lower limbs are commonly known as the arms and legs, respectively (although in academic definitions, these latter terms actually refer only to the upper arm and lower leg). The human arms have relatively great ranges of motion and are highly adapted for grasping and for carrying objects. The extremity of each arm, known as the hand, specializes in intrinsic and digital fine motor skills for precise manipulation of objects. The human legs and their extremities — the feet — are specialized for bipedal locomotion. Compared to most other mammals that walk and run on all four limbs, human limbs are proportionally weaker but very mobile and versatile, and the unique dexterity of the human upper extremities allows them to make sophisticated tools and machines that compensate for the lack of physical strength and endurance. From Wikipedia